- Mission & Vision
-
Labs
- Advanced Concepts Laboratory
- Aerospace, Transportation & Advanced Systems...
- Applied Systems Laboratory
- Cybersecurity, Information Protection and Hardware...
- Electro-Optical Systems Laboratory
- Electronic Systems Laboratory
- Information and Communications Laboratory
- Sensors and Electromagnetic Applications Laboratory
- Facilities
- Leadership
- Ethics & Compliance
- Conference Center
- History >
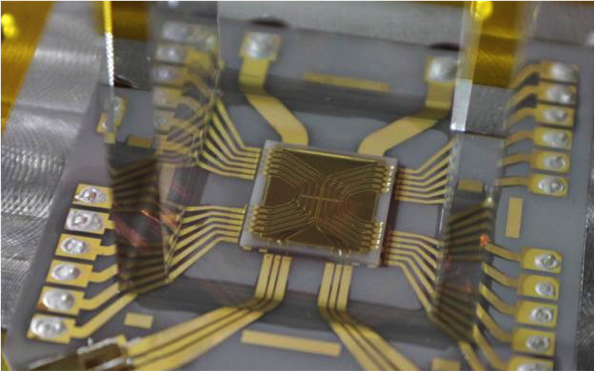
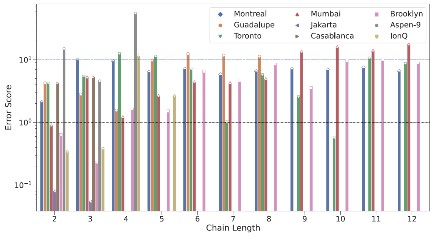
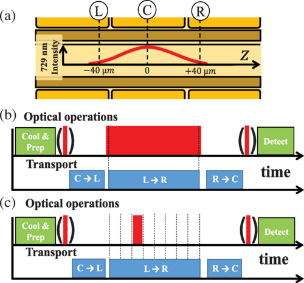
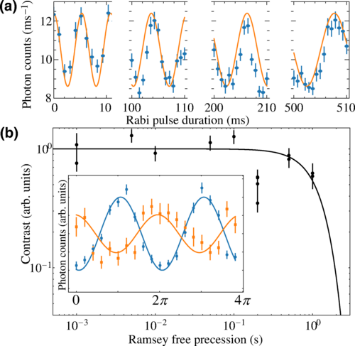
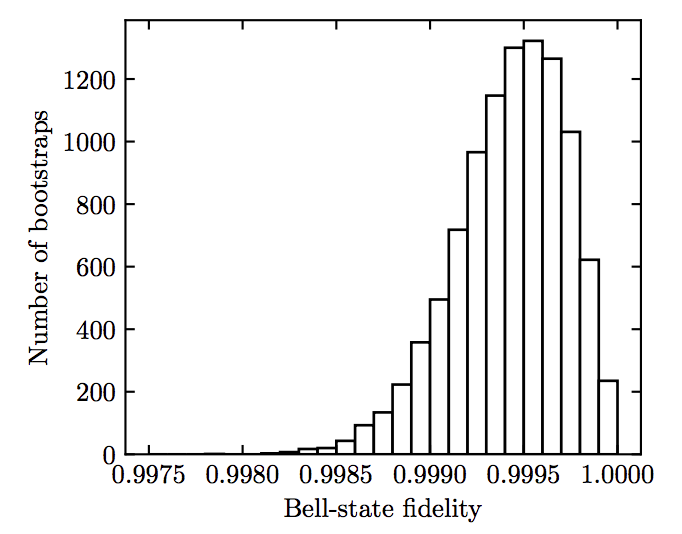
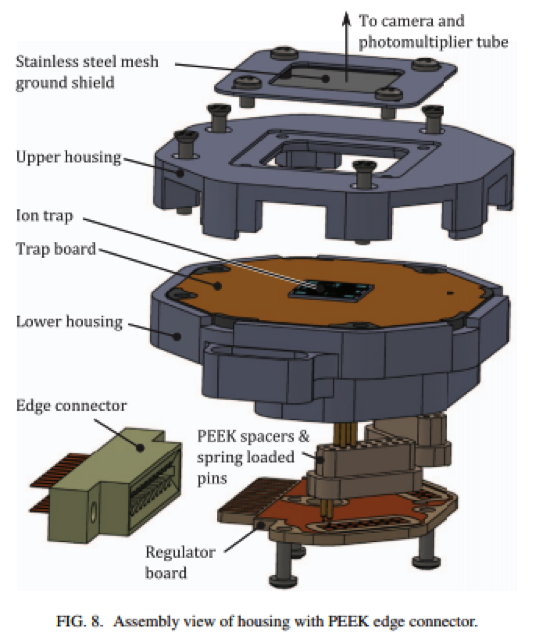
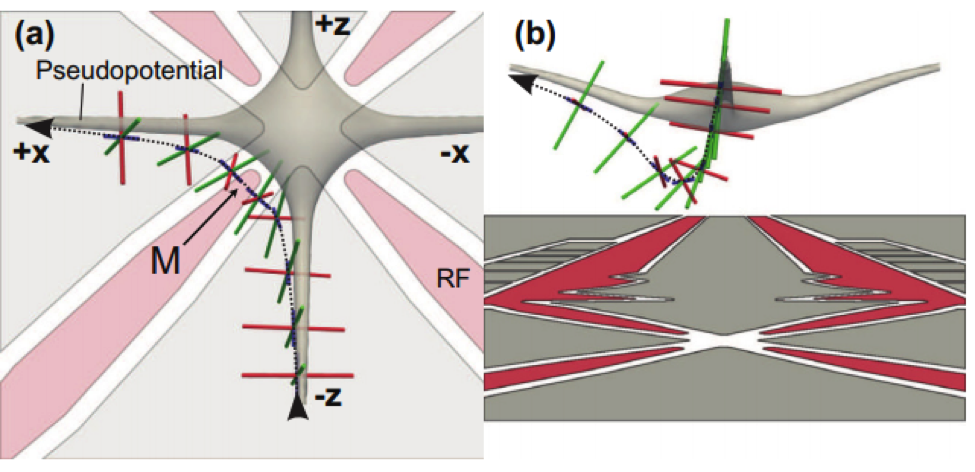
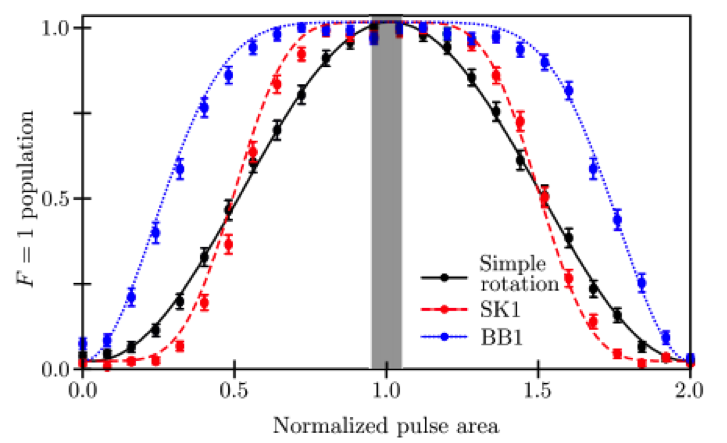
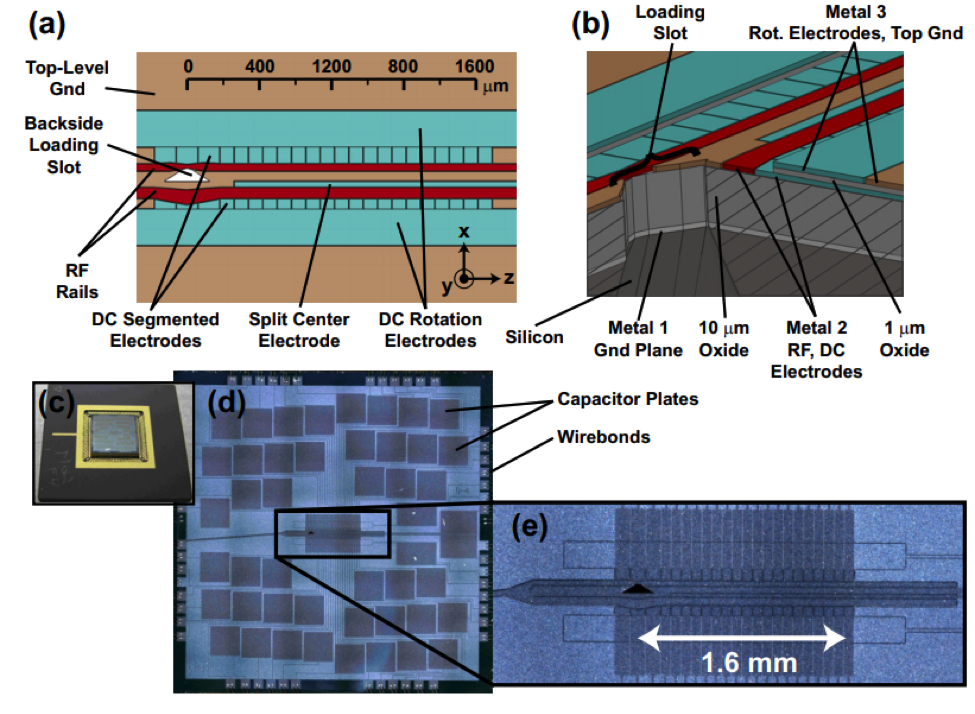
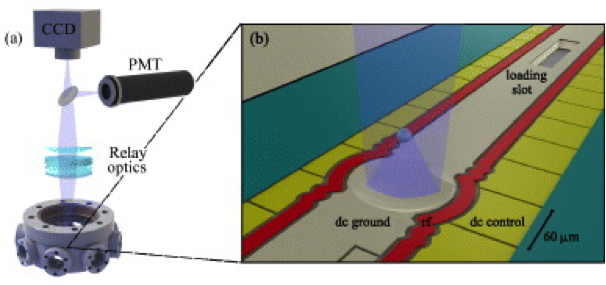
CIPHER’s Quantum Systems Division (QSD) investigates quantum computing systems based on individual trapped atomic ions and novel quantum sensor devices based on atomic systems. QSD has designed, fabricated, and demonstrated a number of ion traps and state-of-the-art components to support integrated quantum information systems. Current efforts focus on implementing small quantum algorithms in these devices with the goal of better understanding the effects of noise on fidelity of the algorithms. Additional topics of investigation include chip-scale atomic magnetometers, atomic clocks, cold-atom gyroscopes, and quantum-secured communications.
Videos and Press
Publications
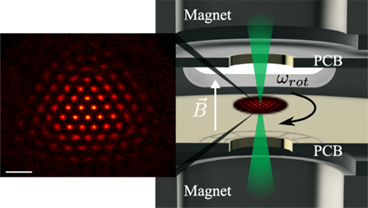
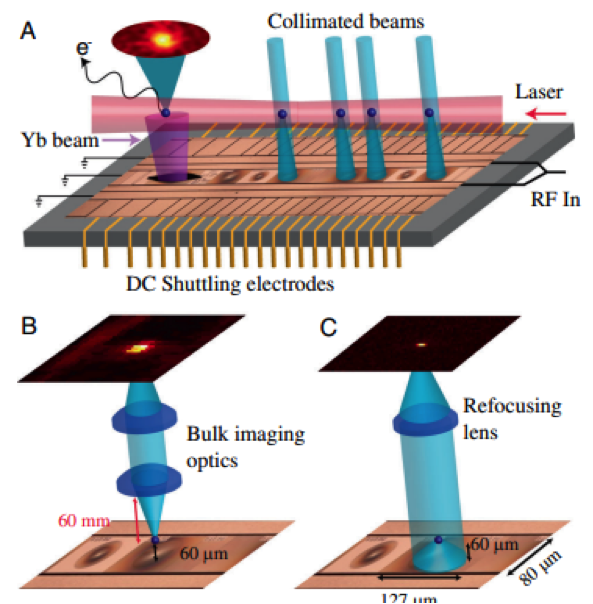
Individual-Ion Addressing and Readout in a Penning Trap
Brian J. McMahon, Kenton R. Brown, Creston D. Herold, and Brian C. Sawyer
Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 173201 (2024)
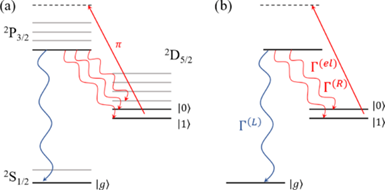
Exactly solvable model of light-scattering errors in quantum simulations with metastable trapped-ion qubits
Phillip C. Lotshaw, Brian C. Sawyer, Creston D. Herold, and Gilles Buchs
Phys. Rev. A 110, L030803 (2024)
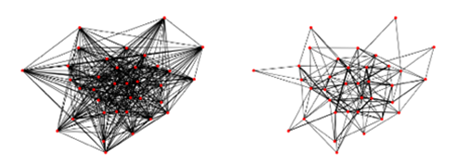
Promise of Graph Sparsification and Decomposition for Noise Reduction in QAOA: Analysis for Trapped-Ion Compilations
Jai Moondra, Phillip C. Lotshaw, Greg Mohler, Swati Gupta
ArXiv:2406.14330 [Quant-Ph] (2024)
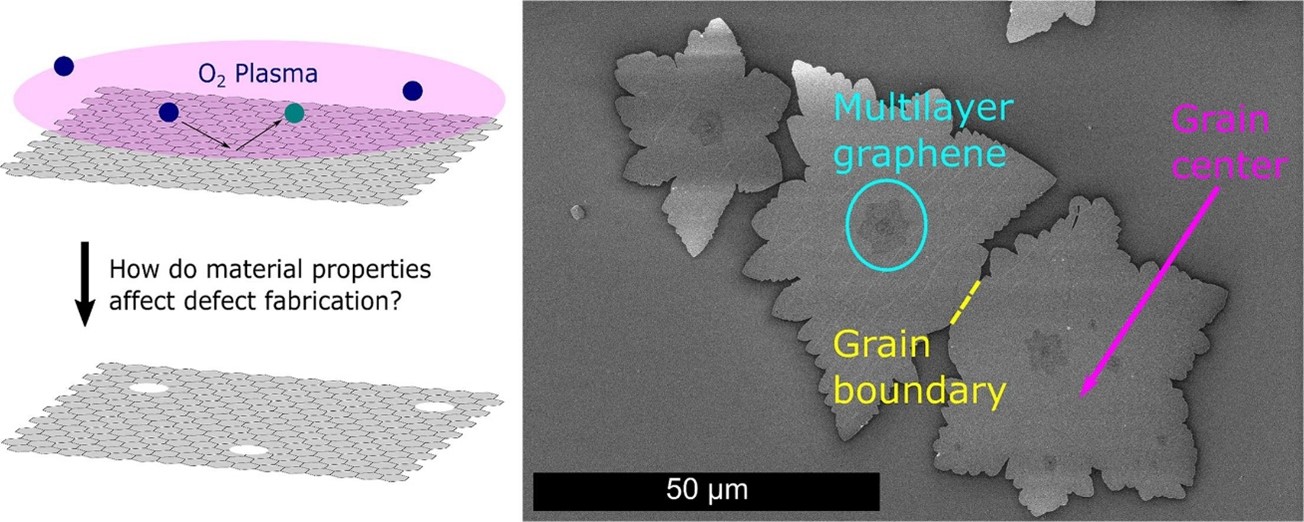
The effects of graphene intrinsic defects on the formation of extrinsic defects by plasma treatment
Katherine Young, Andy Hsiao, and Chris Yang
Applied Surface Science 669 (2024) 160604
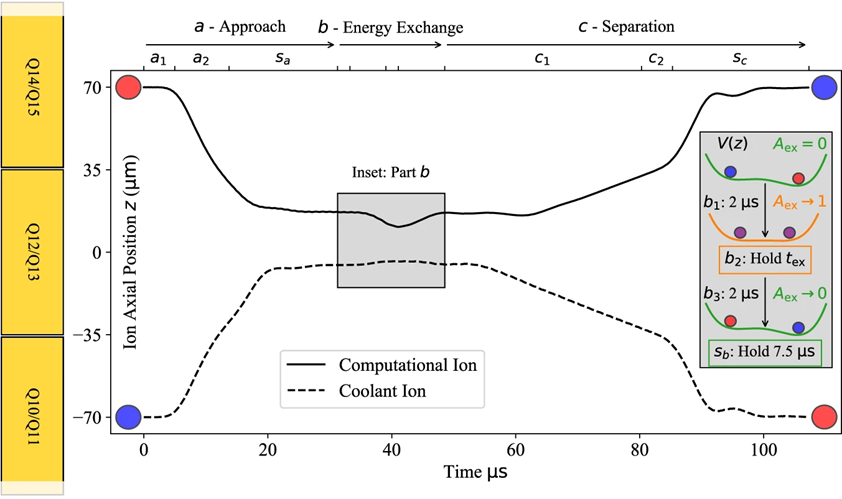
Rapid exchange cooling with trapped ions
Spencer D. Fallek, Vikram S. Sandhu, Ryan A. McGill, John M. Gray, Holly N. Tinkey, Craig R. Clark, and Kenton R. Brown
Nature Communications | (2024) 15:1089
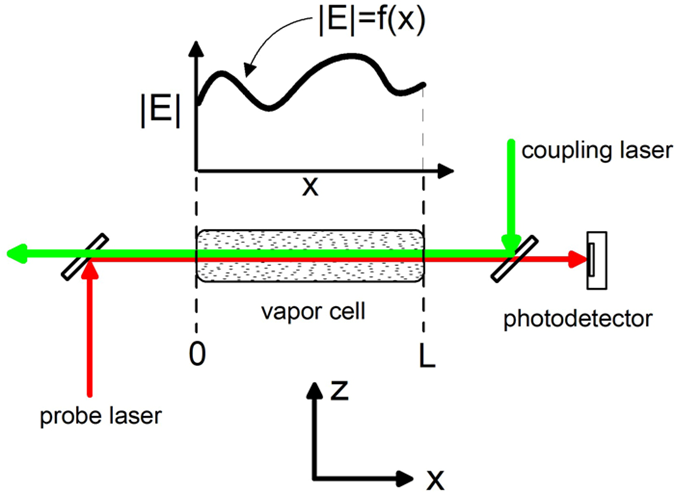
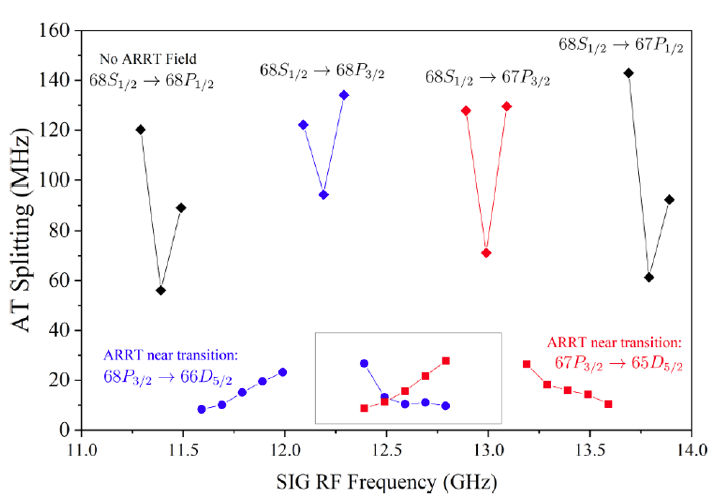
Investigating electromagnetically induced transparency spectral lineshape distortion due to non-uniform fields in Rydberg-atom electrometry
Andrew P. Rotunno, Christopher L. Holloway, Nikunjkumar Prajapati, Samuel Berweger, Alexandra B. Artusio-Glimpse, Roger Brown, Matthew Simons, Amy K. Robinson, Baran N. Kayim, Michael A. Viray, Jasmine F. Jones, Brian C. Sawyer, Robert Wyllie, Thad Walker, Richard W. Ziolkowski, Steven R. Jefferts, Steven Geibel, Jonathan Wheeler, and Eric Imhof
J. Appl. Phys. 134, 084401 (2023)
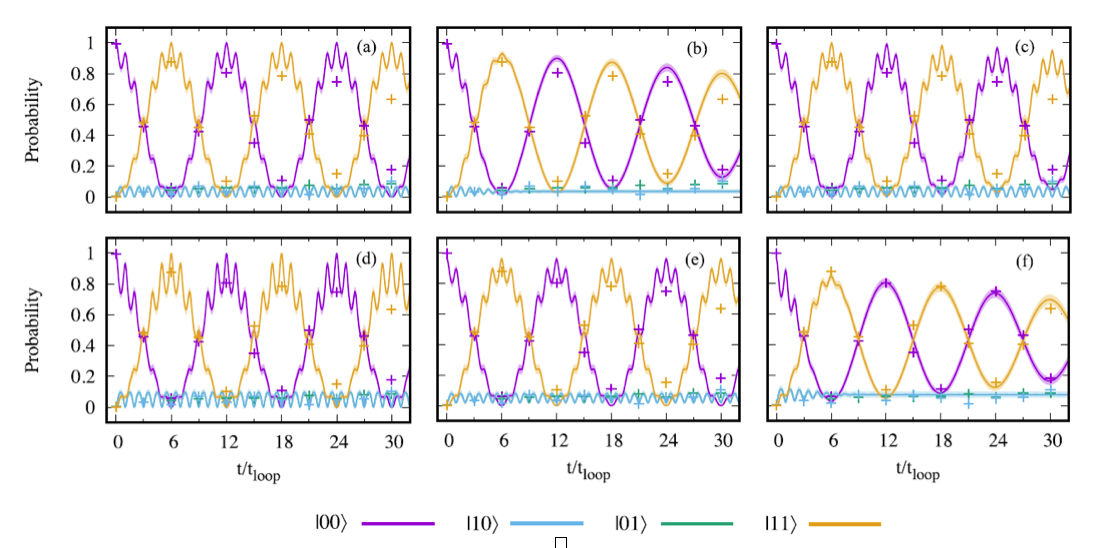
Modeling noise in global Mølmer-Sørensen interactions applied to quantum approximate optimization
Phillip C. Lotshaw, Kevin D. Battles, Bryan Gard, Gilles Buchs, Travis S. Humble, and Creston D. Herold
Phys. Rev. A 107, 062406(2023)
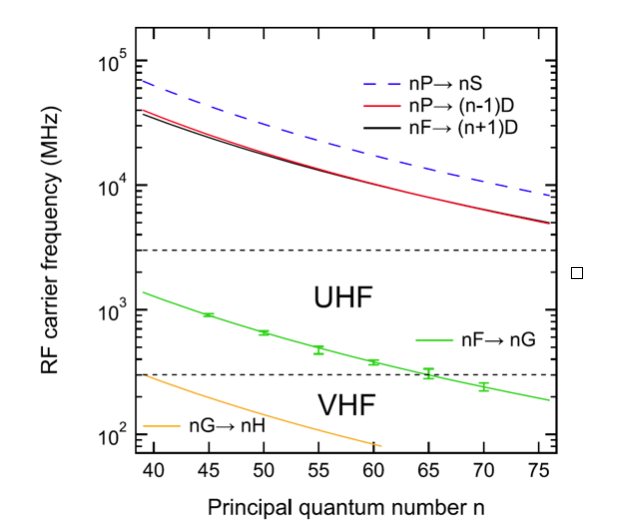
Very-high- and ultrahigh-frequency electric-field detection using high angular momentum Rydberg states
Roger C. Brown, Baran Kayim, Michael A. Viray, Abigail R. Perry, Brian C. Sawyer, and Robert Wyllie
Phys. Rev. A 107, 052605 (2023)
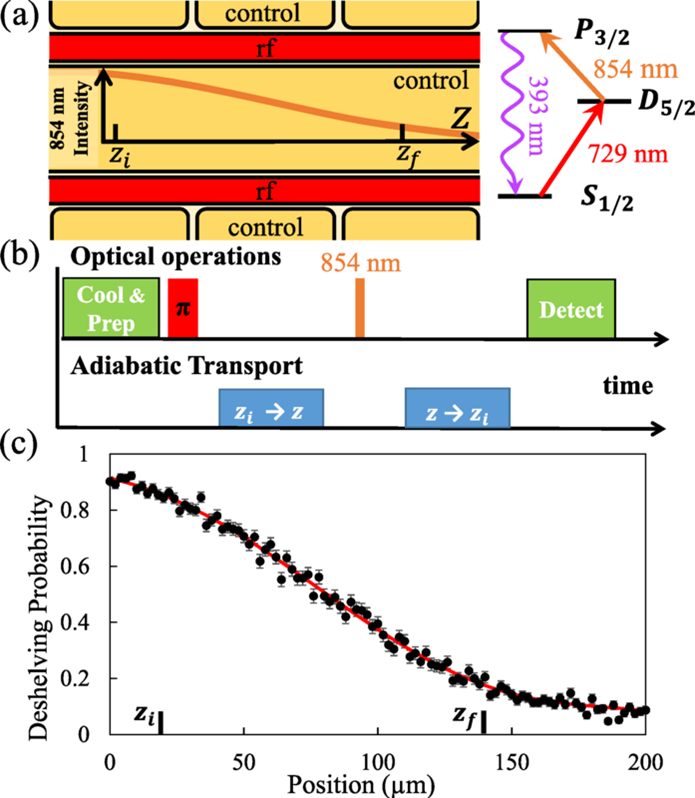
Characterization of fast ion transport via position-dependent optical deshelving
Craig R. Clark, Creston D. Herold, J. True Merrill, Holly N. Tinkey, Wade Rellergert, Robert Clark, Roger Brown, Wesley D. Robertson, Curtis Volin, Kara Maller, Chris Shappert, Brian J. McMahon, Brian C. Sawyer, and Kenton R. Brown
Phys. Rev. A 107, 043119 (2023)
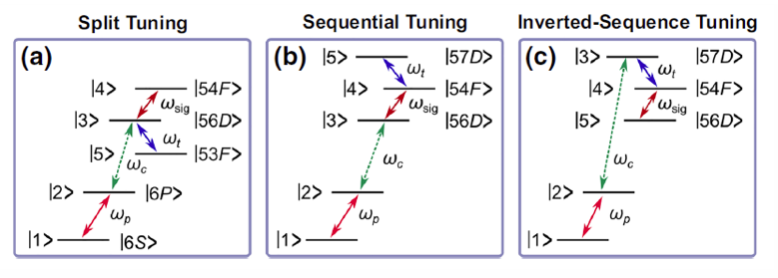
Rydberg-State Engineering: Investigations of Tuning Schemes for Continuous Frequency Sensing
Samuel Berweger, Nikunjkumar Prajapati, Alexandra B. Artusio-Glimpse, Andrew P. Rotunno, Roger Brown, Christopher L. Holloway, Matthew T. Simons, Eric Imhof, Steven R. Jefferts, Baran N. Kayim, Michael A. Viray, Robert Wyllie, Brian C. Sawyer, and Thad G. Walker
Phys. Rev. Applied 19, 044049 (2023)
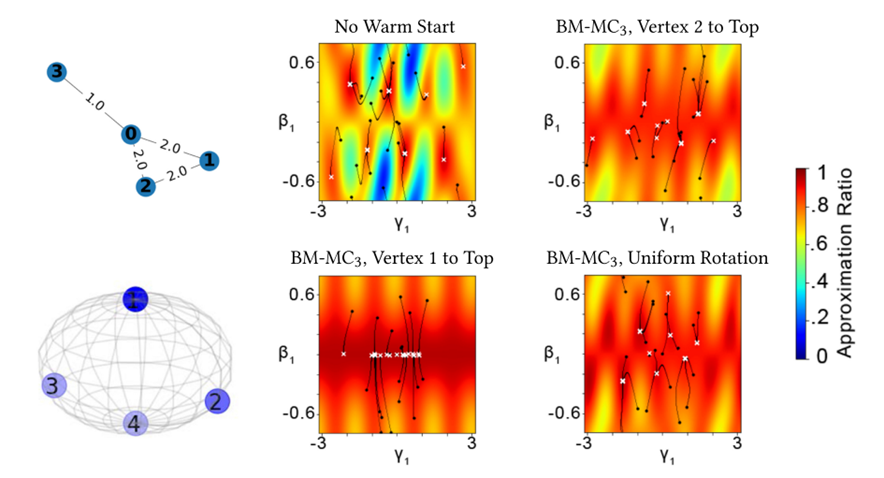
Bridging Classical and Quantum with SDP initialized warm-starts for QAOA
Reuben Tate, Majid Farhadi, Creston Herold, Greg Mohler, and Swati Gupta
ACM Transactions on Quantum Computing, Vol. 4, No. 2, Article 9
Generating target graph couplings for the quantum approximate optimization algorithm from native quantum hardware couplings
Joel Rajakumar, Jai Moondra, Bryan Gard, Swati Gupta, and Creston D. Herold
Phys. Rev. A 106, 022606 (2022)
Classically efficient quantum scalable Fermi-Hubbard benchmark
Bryan T. Gard and Adam M. Meier
Phys. Rev. A. 105, 042602 (2022)
Transport-Enabled Entangling Gate for Trapped Ions
H.N. Tinkey, C.R. Clark, B.C. Sawyer, and K.R. Brown
Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 050502 (2022)
Second-Scale 9Be+ Spin Coherence in a Compact Penning Trap
B. J. McMahon and B.C. Sawyer
Phys. Rev. Applied 17, 014005 (2022)
High-fidelity Bell-state preparation with 40Ca+ optical qubits
C.Clark, H.N. Tinkey, B.C. Sawyer, A.M. Meier, K.A. Burkhardt, C.M. Seck, C.M. Shappert,
N.D. Guise, C.E. Volin, S.D. Fallek, H.T. Hayden, W.G. Rellergert, K.R. Brown,
Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 130505 (2021)
Continuous radio-frequency electric-field detection through adjacent Rydberg resonance tuning
Matthew T. Simons, Alexandra B. Artusio-Glimpse, Christopher L. Holloway, Eric Imhof, Steven R. Jefferts,
Robert Wyllie, Brian C. Sawyer, and Thad G. Walker
Phys. Rev. A 104, 032824 (2021)
Quantum Process Tomography of a Mølmer-Sørensen Gate via a Global Beam
H. N. Tinkey, A. M. Meier, C. R. Clark, C. M. Seck, and K. R. Brown,
Quantum Sci. Technol. 6, 034013 (2021).
Wavelength-Insensitive, Multispecies Entangling Gate for Group-2 Atomic Ions
B. C. Sawyer and K. R. Brown, Phys. Rev. A 103, 022427 (2021).
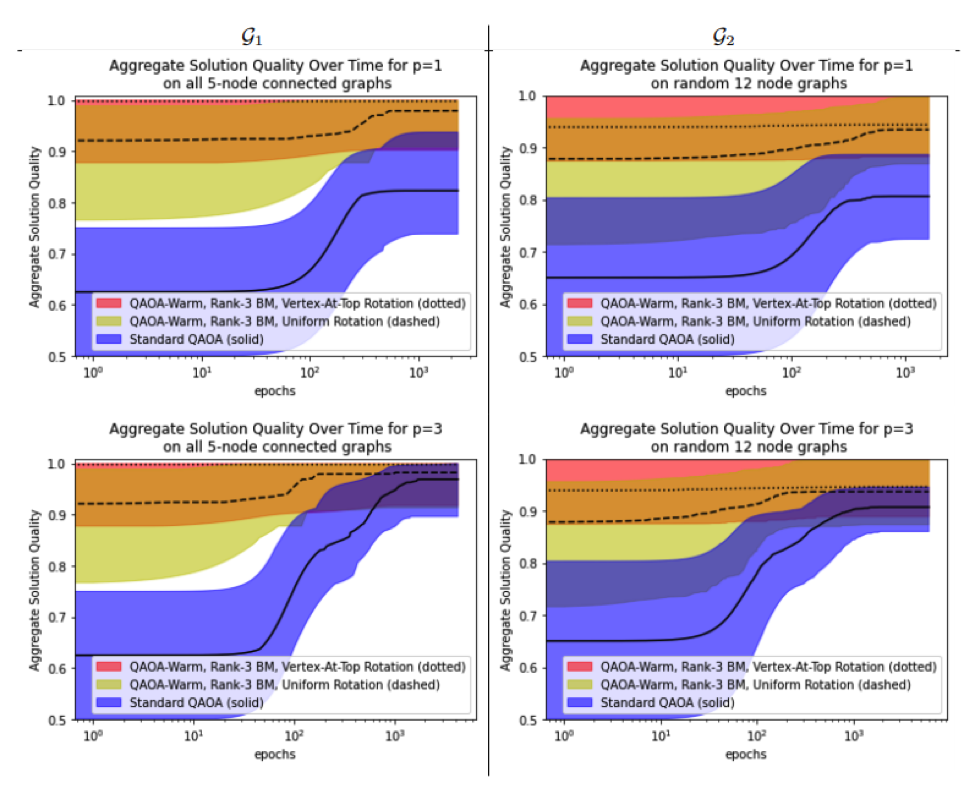
Bridging Classical and Quantum with SDP Initialized Warm-Starts for QAOA
R. Tate, M. Farhadi, C. Herold, G. Mohler, and S. Gupta,
ArXiv:2010.14021 [Quant- Ph] (2020).
Single-Ion Addressing via Trap Potential Modulation in Global Optical Fields
C. M. Seck, A. M. Meier, J. T. Merrill, H. T. Hayden, B. C. Sawyer, C. E. Volin, and
K. R. Brown, New J. Phys. 22, 053024 (2020).
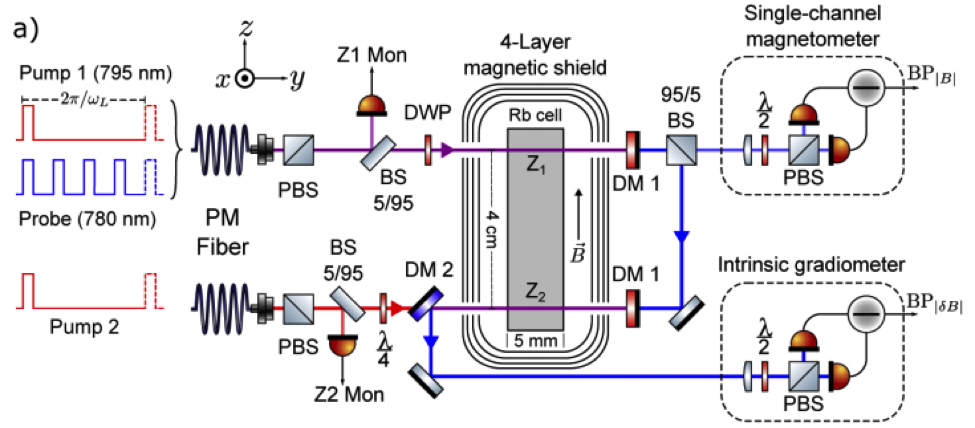
All-Optical Intrinsic Atomic Gradiometer with Sub-20 fT/Hz^0.5 sensitivity in a 22 uT
Earth-Scale Magnetic Field
A. R. Perry, M. D. Bulatowicz, M. D. Bulatowicz, M. Larsen, T. G. Walker, and R. Wyllie,
Opt. Express, OE 28, 36696 (2020).
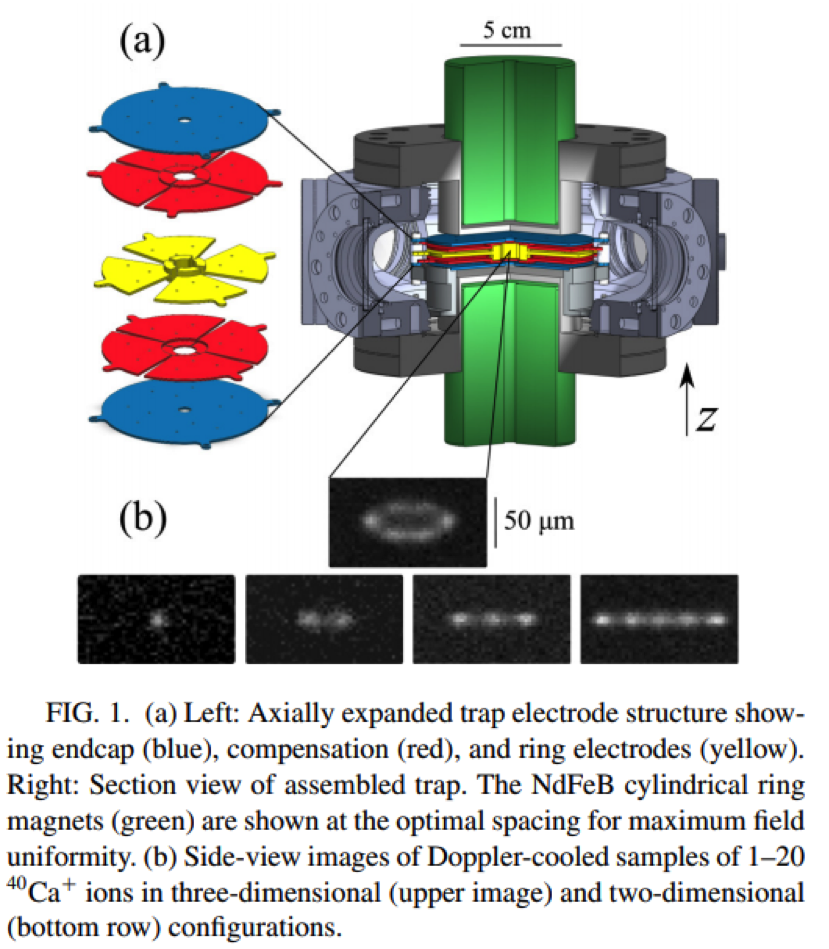
Doppler-Cooled Ions in a Compact Reconfigurable Penning Trap
B. J. McMahon, C. Volin, W. G. Rellergert, and B. C. Sawyer, Phys. Rev. A 101, 013408 (2020).
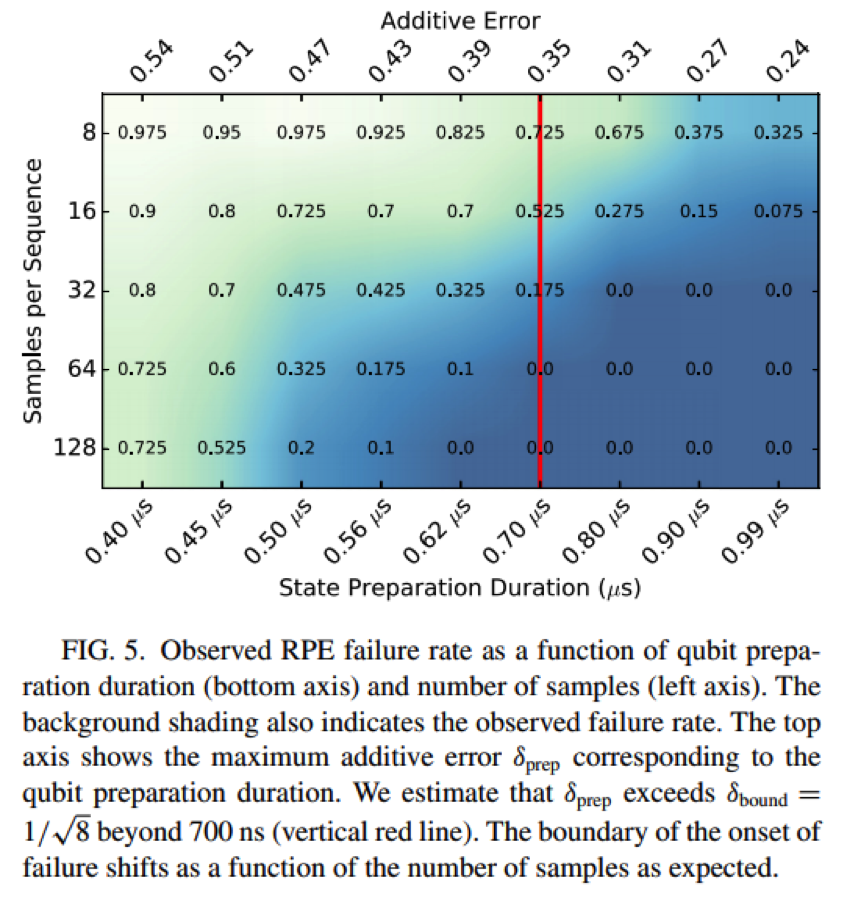
Testing the Robustness of Robust Phase Estimation
A. M. Meier, K. A. Burkhardt, B. J. McMahon, and C. D. Herold, Rev. A 100, 052106 (2019).
Scalable Ion–Photon Quantum Interface Based on Integrated Diffractive Mirrors
M. Ghadimi, V. Blūms, B. G. Norton, P. M. Fisher, S. C. Connell, J. M. Amini, C. Volin,
H. Hayden, C.-S. Pai, D. Kielpinski, M. Lobino, and E. W. Streed,
Npj Quantum Information 3, 4 (2017).
Universal Control of Ion Qubits in a Scalable Microfabricated Planar Trap
C. D. Herold, S. D. Fallek, J. T. Merrill, A. M. Meier, K. R. Brown, C. E. Volin, and J. M. Amini, New J. Phys. 18, 023048 (2016).
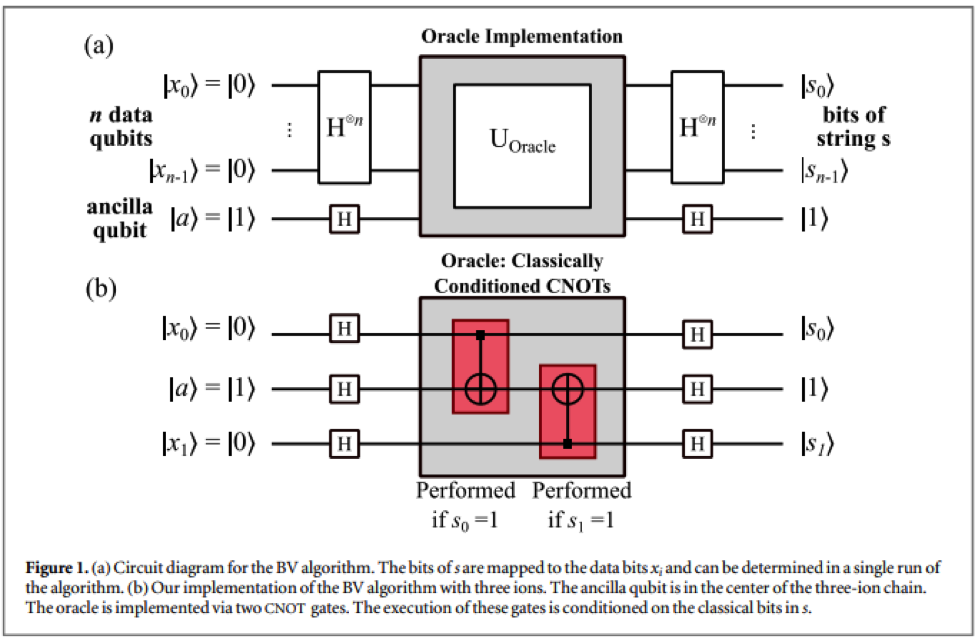
Transport Implementation of the Bernstein–Vazirani Algorithm with Ion Qubits
S. D. Fallek, C. D. Herold, B. J. McMahon, K. M. Maller, K. R. Brown, and J. M. Amini,
New J. Phys. 18, 083030 (2016).
Ball-Grid Array Architecture for Microfabricated Ion Traps
N. D. Guise, S. D. Fallek, K. E. Stevens, K. R. Brown, C. Volin, A. W. Harter, J. M. Amini,
R. E. Higashi, S. T. Lu, H. M. Chanhvongsak, T. A. Nguyen, M. S. Marcus, T. R. Ohnstein, and
D. W. Youngner, Journal of Applied Physics 117, 174901 (2015).
Modulating Carrier and Sideband Coupling Strengths in a Standing-Wave Gate Beam
T. E. deLaubenfels, K. A. Burkhardt, G. Vittorini, J. T. Merrill, K. R. Brown, and J. M. Amini,
JPhys. Rev. A 92, 061402 (2015).
In-Vacuum Active Electronics for Microfabricated Ion Traps
N. D. Guise, S. D. Fallek, H. Hayden, C.-S. Pai, C. Volin, K. R. Brown, J. T. Merrill, A. W.
Harter, J. M. Amini, L. M. Lust, K. Muldoon, D. Carlson, and J. Budach,
Review of Scientific Instruments 85, 063101 (2014).
Reliable Transport through a Microfabricated X -Junction Surface-Electrode Ion Trap
K. Wright, J. M. Amini, D. L. Faircloth, C. Volin, S. C. Doret, H. Hayden, C-S Pai, D. W.
Landgren, D. Denison, T. Killian, R. E. Slusher, and A. W. Harter,
New J. Phys. 15, 033004 (2013).
Spatially Uniform Single-Qubit Gate Operations with near-Field Microwaves and
Composite Pulse Compensation
C. M. Shappert, J. T. Merrill, K. R. Brown, J. M. Amini, C. Volin, S. C. Doret, H. Hayden,
C.-S. Pai, K. R. Brown, and A. W. Harter, New J. Phys. 15, 083053 (2013).
Controlling Trapping Potentials and Stray Electric Fields in a Microfabricated Ion Trap
through Design and Compensation
S. C. Doret, J. M. Amini, K. Wright, C. Volin, T. Killian, A. Ozakin, Douglas Denison,
H. Hayden, C.-S. Pai, R. E. Slusher, and A. W. Harter, New J. Phys. 14, 073012 (2012).
Demonstration of Integrated Microscale Optics in Surface-Electrode Ion Traps
J. T. Merrill, C. Volin, D. Landgren, J. M. Amini, K. Wright, S. C. Doret, C-S Pai, H. Hayden,
T. Killian, D. Faircloth, K. R. Brown, A. W. Harter, and R. E. Slusher,
New J. Phys. 13, 103005 (2011).
People
Division Chief, Quantum System Division, CIPHER